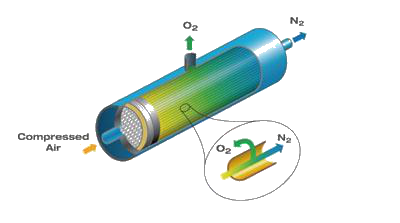
Membrane separation nitrogen generator
Principle of nitrogen production by membrane separation
Membrane separation technology is the use of special selective separation of organic polymers and inorganic materials, the formation of different morphological structure of the membrane, under a certain driving force, the binary or multicomponent components can be separated or enriched due to the different rate of permeation through the membrane.
Take Hollow Fiber Membrane Air Separation for example: Nitrogen, oxygen and water in the air for the membrane material, its penetration rate is different, usually the penetration rate is fast can be called "fast gas" , and the penetration rate is slow can be called "slow gas" . But this "fast" and "slow" is a relative concept. If the oxygen component in the air, relative to water is slow gas, and relative to nitrogen is fast gas, as shown in the right diagram.
When the purified Compressed air enters the air separation membrane, the water and oxygen of the "fast gas" can permeate to the other side of the membrane material more easily through the processes of dissolution, diffusion, infiltration, desorption (or escape) , at the same time, the pressure is reduced, and nitrogen, as a "slow gas" , is exported from the other end of the membrane at a pressure state close to the inlet when it has not penetrated through the membrane wall. In this process, a small amount of nitrogen gas penetrates to the permeation side at low pressure, resulting in a decrease in the nitrogen recovery rate, thus reducing the purity of product nitrogen. The driving force of the physical process of membrane gas separation is the pressure difference between the two sides of the membrane wall.